Algorithm/programmers
[프로그래머스] 행렬 테두리 회전하기
nayeoniee
2022. 10. 30. 14:10
문제
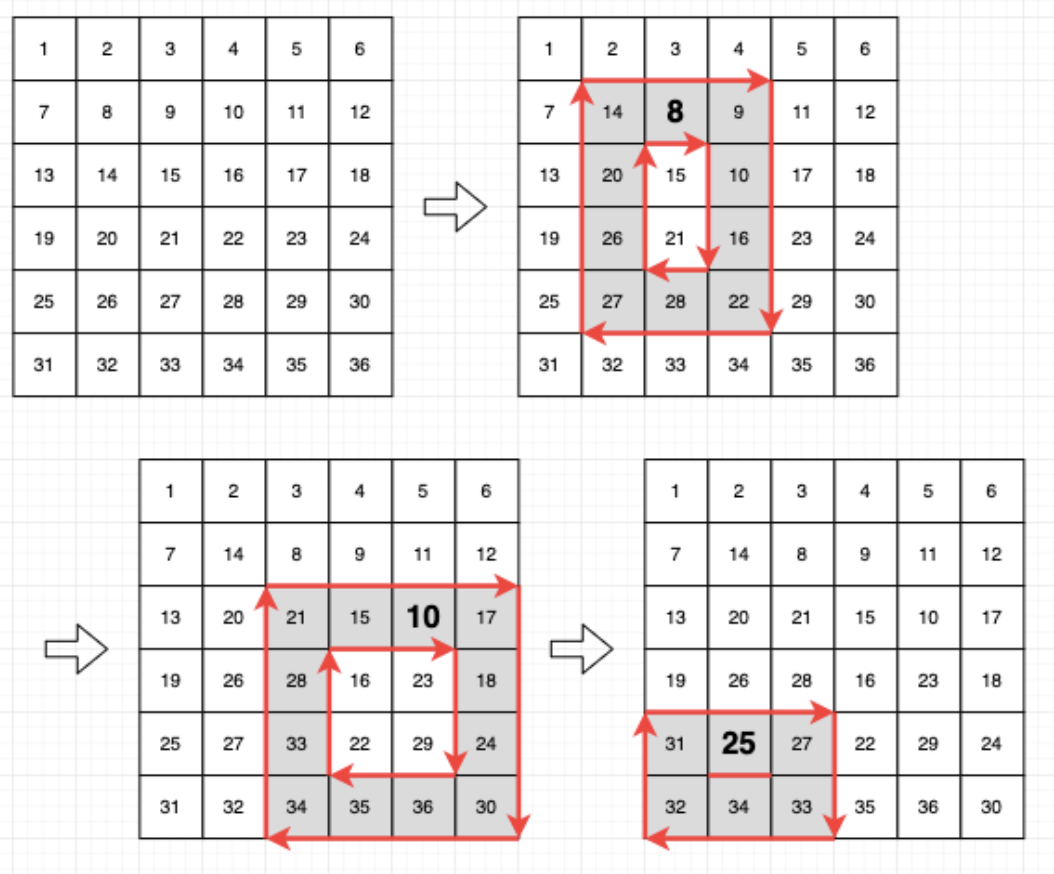
정사각형 혹은 직사각형 형태의 2차원 행렬이 주어지면, 회전 queries에 따라 테두리에 있는 숫자들만 시계 방향으로 1칸씩 회전한다.
각 회전마다 가장 작은 숫자를 구하여라.
아래 예시에서 회전을 3번 하는데 각 회전 당 가장 작은 숫자는 8, 10, 25이다.
프로그래머스
코드 중심의 개발자 채용. 스택 기반의 포지션 매칭. 프로그래머스의 개발자 맞춤형 프로필을 등록하고, 나와 기술 궁합이 잘 맞는 기업들을 매칭 받으세요.
programmers.co.kr
내 풀이
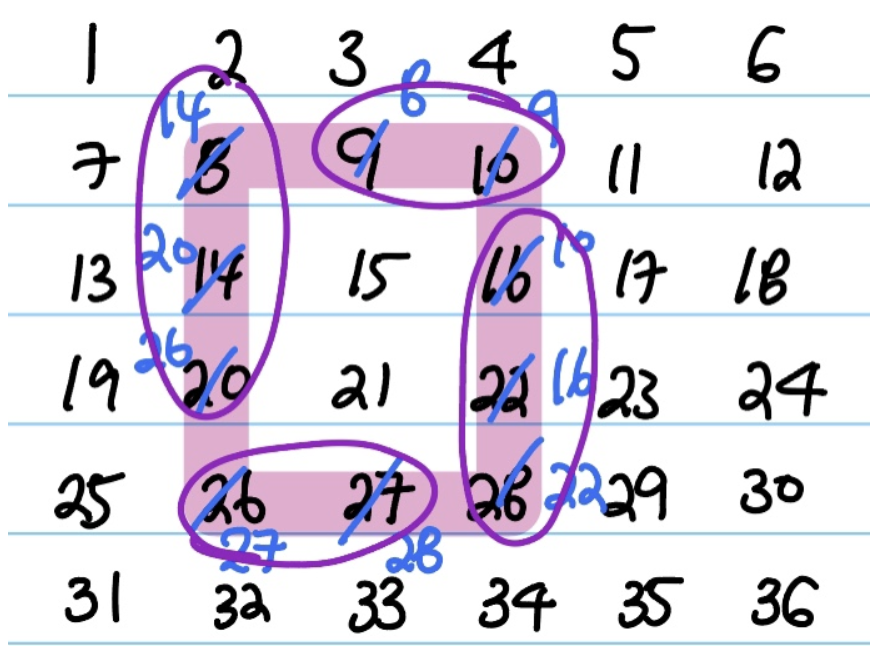
- 처음에 가장자리에 위치한 숫자들을 시계방향으로 이동시키다가, 모서리에 있는 숫자들을 계속 저장해야 한다는 점을 깨달았다.
- 숫자들을 하나씩 시계방향으로 이동하지 않고, 모서리에 있는 숫자가 안 겹치게 하기 위해 그림처럼 4개의 각 묶음 안에서 이동시켰다.
- 각 묶음을 left, top, right, bottom이라고 하면,
- left, bottom은 loop를 순방향으로 접근하고
- top, right는 loop를 역방향으로 접근해야 한다.
- 각 묶음을 left, top, right, bottom이라고 하면,
- left → bottom → right → top 순서로 이동했다.
- 가장 첫 번째 숫자인 nums[xs][ys], 8 값이 날아가기 때문에 변수에 저장했다가 마지막에 변경해주었다.
시간 초과났다….허헣ㅎㅎdeepcopy를 제거해 시간 초과 해결했다.
def solution(rows, columns, queries):
answer = []
nums = []
for r in range(rows):
nums.append([a for a in range(r*columns+1, (r+1)*columns+1)])
def rotate(nums, xs, ys, xe, ye):
tmp = nums[xs][ys]
minimum = tmp
# left
for i in range(xs, xe):
nums[i][ys] = nums[i+1][ys]
minimum = min(minimum, nums[i][ys])
# bottom
for i in range(ys, ye):
nums[xe][i] = nums[xe][i+1]
minimum = min(minimum, nums[xe][i])
# right
for i in range(xe, xs, -1):
nums[i][ye] = nums[i-1][ye]
minimum = min(minimum, nums[i][ye])
# top
for i in range(ye, ys, -1):
nums[xs][i] = nums[xs][i-1]
minimum = min(minimum, nums[xs][i])
nums[xs][ys+1] = tmp
return nums, minimum
for query in queries:
xs = query[0] - 1
ys = query[1] - 1
xe = query[2] - 1
ye = query[3] - 1
out, ans = rotate(nums, xs, ys, xe, ye)
answer.append(ans)
return answer
다른 풀이
* 이 풀이는 C++로 푼 스터디원의 풀이를 파이썬으로 구현했다.
- rows, columns 값에 따라 초기 이중 리스트를 만든다. [[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12] ... [31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36]]
- 회전의 대상이 되는 가장 바깥에 위치하는 숫자들만 순서대로 targets에 넣는다. → 회전 대상이 되는 숫자들만 떼서 해결한게 간단해보인다.
- deque 내장 함수를 사용해 시계방향으로 1칸 이동시킨다. → list를 사용해도 회전할 수 있다. 맨 앞쪽에 숫자를 넣는 appendleft()를 사용하고 싶어서 deque를 사용했다.
- 회전한 숫자를 기존 nums에 넣는다.
from collections import deque
def solution(rows, columns, queries):
answer = []
nums = []
# 초기 이중 리스트 만들기
for r in range(rows):
nums.append([a for a in range(r*columns+1, (r+1)*columns+1)])
def rotate(nums, xs, ys, xe, ye):
# 회전할 숫자 담기
targets = []
for i in range(ys, ye):
targets.append(nums[xs][i])
for i in range(xs, xe):
targets.append(nums[i][ye])
for i in range(ye, ys, -1):
targets.append(nums[xe][i])
for i in range(xe, xs, -1):
targets.append(nums[i][ys])
# 시계 방향으로 1칸 회전
targets = deque(targets)
last = targets.pop()
targets.appendleft(last)
# 회전시킨 숫자 다시 넣기
idx = 0
for i in range(ys, ye):
nums[xs][i] = targets[idx]
idx += 1
for i in range(xs, xe):
nums[i][ye] = targets[idx]
idx += 1
for i in range(ye, ys, -1):
nums[xe][i] = targets[idx]
idx += 1
for i in range(xe, xs, -1):
nums[i][ys] = targets[idx]
idx += 1
return nums, min(targets)
for query in queries:
xs = query[0] - 1
ys = query[1] - 1
xe = query[2] - 1
ye = query[3] - 1
out, small = rotate(nums, xs, ys, xe, ye)
nums = out
answer.append(small)
return answer